Each payment method in international trade has strengths and weaknesses.
For example, open account and cash in advance payments are elementary payment options. They are not only simple, but also inexpensive. However, they inherit high volumes of risks either for the importers or the exporters.
Documentary credits, on the other hand, are relatively secure payment methods, but they are complicated and expensive.
Does international trade finance need another payment method? Can bank payment obligation be the right answer?
Definition of Bank Payment Obligation:
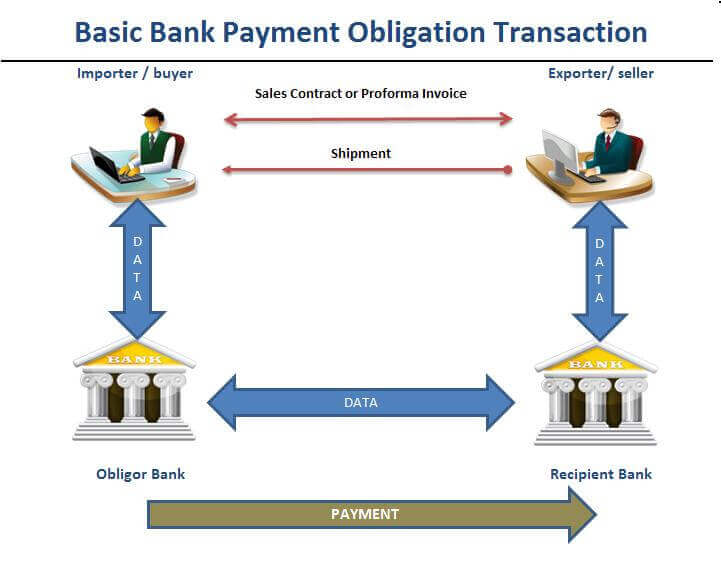
Bank payment obligation (BPO) is an irrevocable undertaking given by an Obligor Bank (typically buyer’s bank) to a Recipient Bank (usually seller’s bank) to pay a specified amount on a agreed date under the condition of successful electronic matching of data according to an industry-wide set of rules adopted by ICC.
Some Important Definitions under Bank Payment Obligation (BPO):
- “Obligor bank” means buyer’s bank under Bank Payment Obligations. Obligor bank issues the legally binding, valid, irrevocable but conditional and enforceable payment undertaking to Recipient Bank. Obligor bank is an equivalent term of issuing bank under letters of credit definitions.
- “Recipient Bank” means seller’s bank under Bank Payment Obligations.
- “Trade Services Utility” (TSU) means a centralized matching and workflow engine providing timely and accurate comparison of data taken from underlying corporate purchase agreements and related documents, such as commercial invoices, transport and insurance.
- The URBPO, the Uniform Rules for Bank Payment Obligations ICC publication No. 750, are the rules of Bank Payment Obligation adopted by ICC banking commission.
How Does Bank Payment Obligation Work?
Bank payment obligation and letter of credit have some characteristics in common.
Firstly banks play a key role on both payment methods. Secondly banks are giving the irrevocable payment undertaking.
Figure 1 : Basic Bank Payment Obligation Transaction
Bank Payment Obligation (BPO) has been established on two main expectations,
- The use of minimum fields, the buyer, the seller and respective banks agree on the payment terms and conditions and on the minimum trade information required to assess the credit risk;
- The dispatch of documents, such as the bill of lading, certificate of origin and certificate of quality, from the seller directly to the buyer.
Given the limited information required by the banks and the accelerated document exchange, companies should expect a lower rate of discrepancies and an acceleration of the settlement process.
Figure 2 : Bank Payment Obligation Transaction Flow in Detail
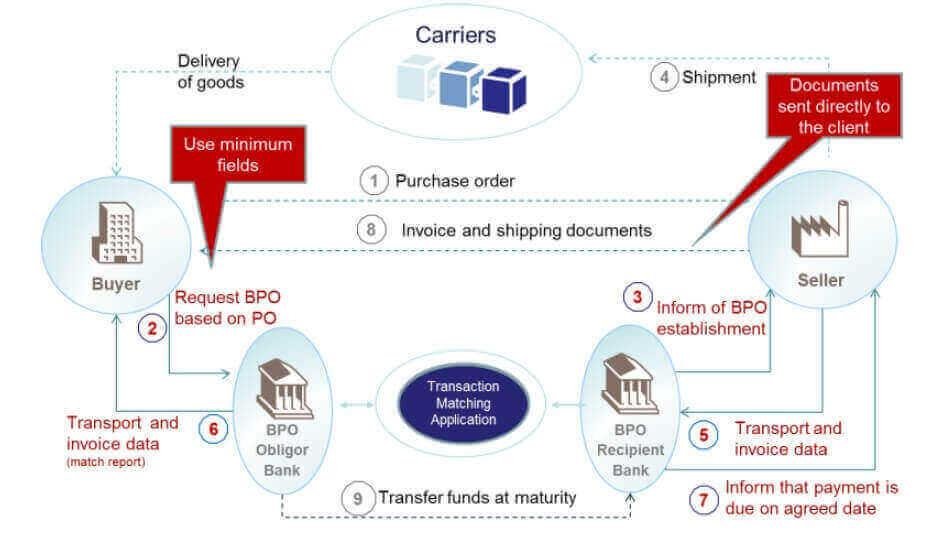
Step-by Step Bank Payment Obligation Transaction
Baseline Establishment
- Step 1 : Buyer and seller agreed on BPO (bank payment obligation) as a payment term on the sales contract. Buyer send its purchase order to the seller.
- Step 2 : Buyer provides the minimum data from the purchase order and conditions of the bank payment obligation to the obligor bank.
- Step 3 : Seller confirms the data from the PO and send its acceptance of the BPO conditions to the recipient bank. If both buyer’s and seller’s data are matched on the Transaction Matching Application than the baseline is established. Both buyer and seller will be receiving a matching reports from their banks.
BPO is irrevocable but conditional payment method. (payment is subject to the electronic matching of agreed data-sets)
Matching
- Step 4 : Seller ships the goods as agreed on the sales contract.
- Step 5 :Seller presents the shipment data and invoice data to its bank, which submits it to Transaction Matching Application for matching.
- Step 6 : Buyer receives a match report from its bank. Buyer is invited to accept any mismatches if any.
- Step 7 : Seller’s bank inform seller about the successful data-set match.
BPO becomes operative and due according to the agreed payment terms.
Settlement
- Step 8 : Seller sends the trade documents directly to the buyer. Buyer will clear goods from the customs with these documents.
- Step 9 : On the due date, the obligor bank debits the proceeds from buyer’s account
Bank Payment Obligation Video Presentation
Bank payment obligation (BPO) is the newest payment method in international trade.
Exporters , importers and bank professionals need learning material to understand its usage.
On this page you can find bank payment obligation video presentation. It is prepared by Commerzbank, one of the world’s leading banks in international trade services solutions sector.
What are the Advantages of the BPO (Bank payment Obligation) for the Exporters?
- Bank payment obligation is a secure payment method in international trade for the exporters. BPO can be more secure than the letter of credit, because the documents will not be checked by human beings, by which process eliminating alleged discrepancy risks.
- The bank payment obligation is cheaper than letter of credit.
- Exporters could get their money very fast from the banks under the BPO transactions as documents are checked by an automatic system instantly.
- Exporters have more control over the goods until they have been paid by the banks under the BPO transactions as shipment documents will be held by the exporters during the BPO process. Exporters do not send paper documents to the banks. Once exporters receive their money from the banks, they dispatch the documents to the importers separately.
- Exporters could reach pre-shipment and post-shipment finance in BPO transactions.
- Once the bank payment obligation is opened, it is almost impossible for the importer to cancel the order without the consent of the exporter.
- Non-payment risk shifts from importer to importer’s bank, which is called obligor bank in the BPO transaction.
What are the Advantages of the BPO (Bank payment Obligation) for the Importers?
- As a payment method the bank payment obligation is more secure than the advance payment, because the BPO is a conditional payment method. Under the BPO transactions, banks send payment amounts to the exporters only after the shipment of the goods, not before.
- Issuing a bank payment obligation may prove that the importer is a financially secure and strong company.
- The Bank payment obligation is an irrevocable payment method like the letter of credit. As a result importers can convince exporters to make shipments with the BPO much more easily comparing to open account or documentary collections.
- The BPO facilitates financing of the shipment for the importers.
- It is possible for the importers to pay the transaction amount after receiving the shipment, if a deferred payment has been agreed upon such as “60 days after match”, “90 days after match” etc.
- The BPO may protect the buyers, at least in theory, against non-shipments, late shipments and inferior quality of goods shipments.
Bank Payment Obligation – Comparison to Letter of Credit and Open Account
Bank Payment Obligation Comparison to Letter of Credit:
- Both bank payment obligation and letter of credit have an irrevocable structure.
- Bank payment obligation and letter of credit are governed by ICC rules. BPO rules are URBPO, letters of credit rules are UCPDC.
- The conditional payment guarantee is given by a bank to another bank in BPO transactions. BPO is a bank-to-bank payment obligation. The conditional payment guarantee is given by a bank to a commercial company in L/C transactions. (Letters of credit can be issued bank-to-bank transactions as well.)
- Letter of credit is paper intensive. BPO is an electronic payment method.
- Documents have been checked by banks’ staff manually under letter of credit transactions. Data match completed by online means under BPO transactions.
- Under BPO transactions shipment documents would not be sent to the banks.
- Letter of credit is slow and expensive. BPO is fast and not as expensive as L/Cs.
Bank Payment Obligation Comparison to Open Account:
- Both bank payment obligation and open account are fast and easy to handle.
- Open account is the riskiest payment method for the exporters. Nonpayment risk is stemmed from the importer and must be covered by the exporter in full under open account payments. On the contrary, under the BPO the obligor bank is the entity that is giving the payment guarantee to the exporter through the recipient bank. As a result non-payment risk mitigates from the importer to the importer’s bank under BPO transactions.
- There are no rules exist for open account payments. On the other hand bank payment obligations can be issued subject to the URBPO 750.
- Under open account transactions exporters must finance importers, whereas they can be benefited pre-shipment finance and post-shipment finance under the BPO.
Sources:
- Bank Payment Obligation A new payment method, July 2016, SWIFT’s Corporate and Supply Chain Market Management team,
- Bank Payment Obligation – Comparison To Letter Of Credit And Open Account, J.P. Morgan,