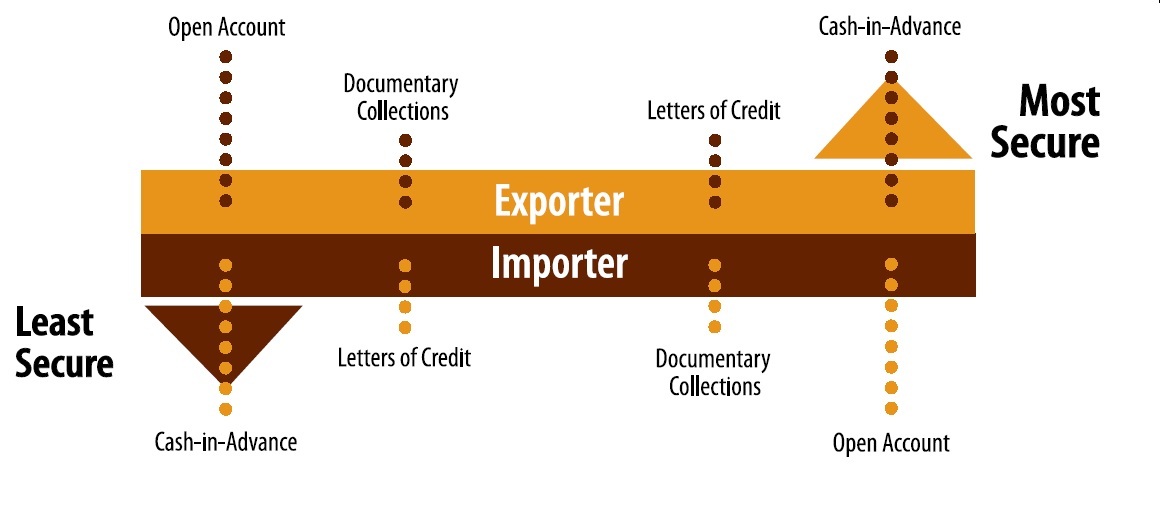
There are 5 types of payment methods available in international trade.
These payment types are cash-in-advance, open account, documentary collections, documentary credits (letters of credit) and bank payment obligation.
Short Descriptions of International Payment Methods:
Cash-in-Advance: Cash in advance is a payment method in international trade in which an order is not processed until full payment is received by the supplier in advance.
Sometimes cash in advance is called cash with order.
Please always keep in mind that under the cash in advance payment, the funds received by the exporters before the ownership of the goods is transferred to the importers.
Cash in advance posses highest risk to the importer, lowest risk to the exporter.
Open Account: Open account means that buyers pay the cost of the goods after goods have been shipped by the supplier.
In an international trade transaction open account defines as a sale where the goods are shipped and/or delivered before payment is due, which is usually in 30 or 60 days.
Open account posses highest risk to the exporter, lowest risk to the importer.
Documentary Collections: International trade procedure in which a bank in the importer’s country acts on behalf of an exporter for collecting and remitting payment for a shipment.
The exporter presents the shipping and collection documents to his or her bank (in own country) which sends them to its correspondent bank in the importer’s country.
The foreign bank (called the presenting bank) hands over shipping and title documents (required for taking delivery of the shipment) to the importer in exchange for
- cash payment (in case of ‘documents against payment‘ instructions) or
- a firm commitment to pay on a fixed date (in case of ‘documents against acceptance‘ instructions).
A documentary collection (D/C) is a transaction whereby the exporter entrusts the collection of a payment to the remitting bank (exporter’s bank), which sends documents to a collecting bank (importer’s bank), along with instructions for payment.
Funds are received from the importer and remitted to the exporter through the banks involved in the collection in exchange for those documents.
Documentary Credits: Documentary credits, also known as letters of credit, are one of the payment methods in international trade.
Letter of credit defined by International Chamber of Commerce publication of UCP 600 as “any arrangement, however named or described, that is irrevocable and thereby constitutes a definite undertaking of the issuing bank to honour a complying presentation.”
Bank Payment Obligation: Bank payment obligation is a new payment method in international trade.
Bank payment obligation (BPO) is an irrevocable undertaking given by an Obligor Bank (typically buyer’s bank) to a Recipient Bank (usually seller’s bank) to pay a specified amount on a agreed date under the condition of successful electronic matching of data according to an industry-wide set of rules adopted by ICC.
What are the Key Points of Consideration When Choosing an International Payment Method?
Financial Needs of the Parties: Open account payment term is a credit granted by the exporter in favor of the importer. In contrast, cash in advance is a credit granted by the importer in favor of the exporter.
Letters of credit available by deferred payment and documentary collections payable with time drafts are also financial credits supplied to the buyers.
For these reasons financial needs of the parties is a key element determining the payment terms in international trade transactions.
Negotiation Power of the Parties: Sometimes exporters are in pressure to sell their products. On the other hand, importers are desperate to find a particular good in a short period of time.
If balance of the trade power diminishes in favor of one party, then the stronger party may want to benefited from the situation and dictates most favorable payments terms.
Country Risk of the Exporter and the Importer: As an example if the importer residents in a developed country whereas the exporter sits in a risky country, then the importer may do not want to take risks and choose the most secure payment method for himself.
Sector of the Transaction Parties: Occupying sector of the exporter and the importer is one of the most influencing element that effects the determination of the payment method. For example, food and textile sector practicing open account payments or documentary collections, on contrary oil sector uses letters of credit.
Willingness to Take Risks of the Parties: Willingness to take risks is one of the key factor determining the payment method in international trade.
Occasionally exporters want to take extra risk, while importers tend to trust their suppliers.
A risk taking exporter may ship the goods against open account terms whereas a risk taking importer may decide to pay in advance.
If both parties want to limit their risks, then they should either choose documentary collections or documentary credits.
Legal Legislation: If you want to export to Algeria, you have to choose either documentary collections or letters of credit as a payment method. This is an Algerian legislation and every exporter that makes business with Algeria has to obey this rule.
“At the beginning of August 2009, the Algerian government released the ‘Complementary Finance Law 2009’ which decreed that all imports into the country, with a value exceeding $1000, would require a documentary letter of credit (LC)”
Source: http://www.tradefinancemagazine.com/Article/2471154/LC-boom-in-Algeria.html
Country Practices: Middle East countries tend to use letters of credit intensely, when importing goods. Chinese exporters also use letters of credit in great volumes. USA importers using documentary collections for small value purchases. German importers would like to pay 30 days after bill of lading date under open account payment terms.
