History of Freight Containers:
Standardization is one of the key elements of our modern civilization. By standardization we increase productivity, decrease costs and improve quality of the goods and services.
Standardization changed almost every sector more or less, but it has an huge impact to the international transportation by means of containerization.
The pattern of cargo reception and shipment has dramatically changed with the use of the freight container.
The use of containers, which started more than 50 years ago, in intercontinental traffic is now available in most seaports worldwide.
In the 1960’s, many seaports either had inadequate container facility or none at all. Consequently, export shipments often relied on conventional (break-bulk) vessels.
The cargoes were placed alongside a vessel for hoisting on board. The stevedores (longshoremen) were often employed to carry cargoes on and off the vessel.
The loading and unloading of vessels consumed too much time, which caused dockside bottlenecks and delayed shipments. With the increased use of containers, the congestion was decentralized.
The problem of congestion was transferred from the docks or piers to the container freight stations or terminals. (1)
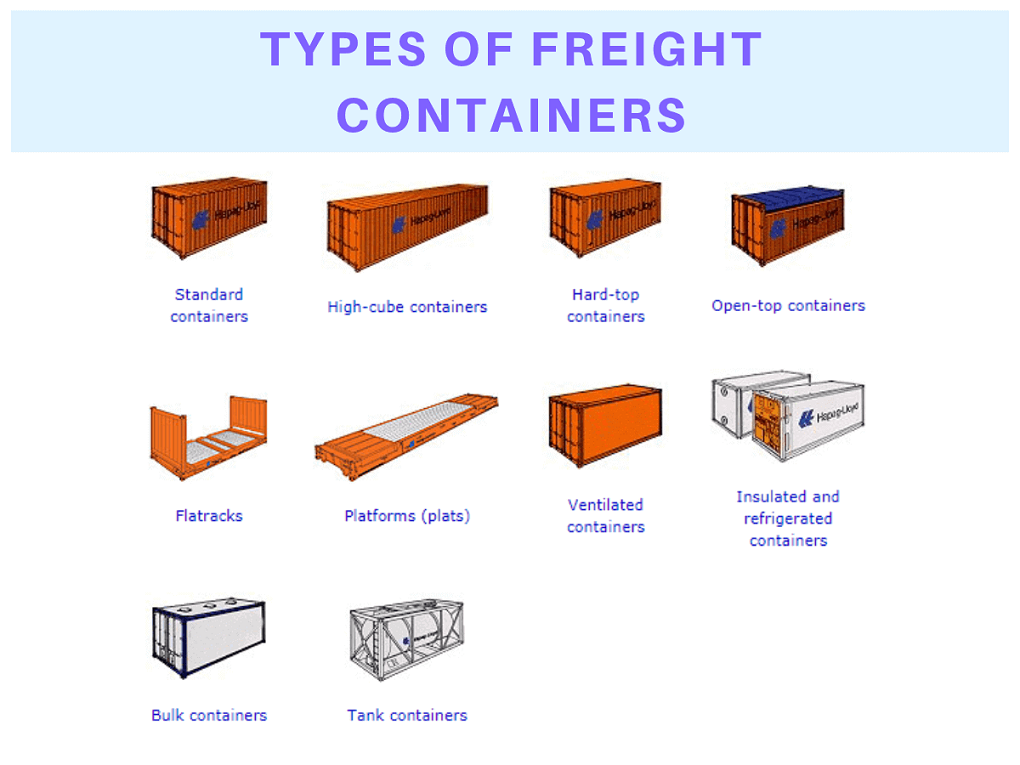
Classification of Freight Containers:
Containers are available in configurations to take almost every kind of cargo and mode of transportation (ocean, air, road, and rail). (2)
Dry Containers:
 A dry container is a type of freight container, totally enclosed and weatherproof, with a rigid roof, rigid side walls, and floor, having at least one of its end walls equipped with doors and intended to be suitable for the transport of cargo of the greatest possible variety.
A dry container is a type of freight container, totally enclosed and weatherproof, with a rigid roof, rigid side walls, and floor, having at least one of its end walls equipped with doors and intended to be suitable for the transport of cargo of the greatest possible variety.
This is by far the most common type of container. It is suitable for the carriage of most types of “Dry” goods, including those packed in boxes, cartons, cases, bags, bales, pallets, drums etc. (3)
Dry container are available with standard height and high cube formations. The internal height of standard dry containers are 2395 mm (7′ 10 1/4″) whereas the internal height of high cube containers are 2700 mm (8′ 10 1/4″)
Dry Container Dimensions: 20′ Dry Container, 40′ Dry Container, 40′ Dry High Cube and 45′ Dry High Cube dimensions.
What are the Differences Between 40′ Standard Dry Containers and 40′ High-Cube Dry Containers?
On this post you can find the differences between a 40′ Standard Dry Container and a 40′ High-Cube Dry Container in terms of external dimensions, internal dimensions and allowed payloads.
Pallet Wide Containers: 20′, 40′ and 45′ Pallet Wide Dry Containers
Pallet wide containers introduced to eliminate inefficiency in the palletized container shipments. It is possible to load two or three pallets side by side to these containers.
PALLET LOADING PLANS FOR DRY CONTAINERS
How Many Pallets Fit in a 20′ Container?
On this post I am explaining how many Euro pallets (1200 mm x 800 mm) and Industrial Pallets (1200 mm x 1000 mm) fit in to a 20′ standard dry container.
How Many Pallets Fit in a 40′ Container?
On this post I will explain how many Euro pallets (1200 mm x 800 mm) and Industrial Pallets (1200 mm x 1000 mm) fit in to a 40′ standard dry container.
How Many Pallets Fit in a 40′ High-Cube Container?
On this post I will explain how many Euro pallets (1200 mm x 800 mm) and Industrial Pallets (1200 mm x 1000 mm) fit in to a 40′ high-cube dry container.
Refrigerated Containers (Reefer Containers):
 A refrigerated container is a type of container which is equipped with an electrical appliance (mechanical compressor) for the purposes of cooling or heating the air within the container.
A refrigerated container is a type of container which is equipped with an electrical appliance (mechanical compressor) for the purposes of cooling or heating the air within the container.
Refrigerated containers designed for the transport of perishable goods in a temperature-controlled environment (from -35°C to +35°C). (4)
What kind of goods should be shipped with reefer containers?
Generally foodstuff and some pharmaceuticals are transported via reefer containers.
- Fresh Vegetables and Fruits: Lychees, grapes, grapefruits, mango, avocados, bananas, kiwi, apples, stone fruits etc.
- Frozen Vegetables and Fruits: IQF frozen vegetables and fruits such as IQF ocras, IQF artichokes, IQF spinach, IQF green peas, IQF Strawberry, IQF Figs, IQF Apricots etc.
- Fresh Fish: Fresh seabass, fresh sea bream, fresh sea trout, fresh pangasius, frozen sea food etc.
- Frozen Fish: IQF seabass, IQF sea bream, IQF sea trout, IQF pangasius, IQF frozen sea food etc.
- Other Foodstuff: Chilled and frozen meat, milk and dairy products, margarine, egg, juice and concentrate, chocolate, butter etc.
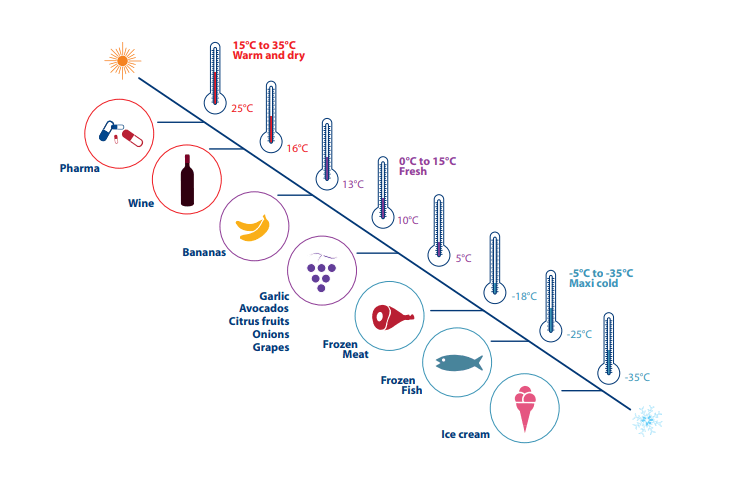
On above image you can see some foodstuff which are transported via reefer containers and corresponding optimum transportation temperatures.
Reefer Container Dimensions: 20′ Reefer Container and 40′ Reefer High Cube dimensions.
PALLET LOADING PLANS FOR REEFER CONTAINERS
How Many Pallets Fit in a 20′ Reefer Container?
On this post I will explain how many Euro pallets (1200 mm x 800 mm) and Industrial Pallets (1200 mm x 1000 mm) fit in to a 20′ reefer container.
How Many Pallets Fit in a 40′ High-Cube Reefer Container?
On this post I will explain how many Euro pallets (1200 mm x 800 mm) and Industrial Pallets (1200 mm x 1000 mm) fit in to a 40′ high-cube reefer container.
Hardtop Containers:
 Hardtop container shares common features with standard dry container, except that it has a removable steel roof.
Hardtop container shares common features with standard dry container, except that it has a removable steel roof.
The walls of hard-top containers are generally made of corrugated steel. The floor is made of wood.
Removable steel roof of some hardtop containers has points for accommodating forklift trucks, allowing the roof to be lifted by forklift. The roof weighs approx. 450 kg. In addition, the door header may be swing out. (6)
Hardtop Container Dimensions: 20′ Hardtop Container, 40′ Hardtop Container and 40′ Hardtop High Cube Container dimensions.
Open-Top Containers:
 Open-top container is a type of a freight container which has no rigid roof, but has a flexible and movable or removable cover.
Open-top container is a type of a freight container which has no rigid roof, but has a flexible and movable or removable cover.
Such containers may have movable or removable top end transverse members above their end doors.
Open-top containers are primarily used to carry heavy and/or bulky finished products, which handling and loading can only be performed with a crane or a rolling bridge.
Tiltable half-height open top containers are specially designed to carry bulk minerals.
Open-Top Container Dimensions: 20′ Open Top Container, 40′ Open Top Container and
40′ Open Top High Cube Container dimensions.
Flatrack Containers:
 Flatrack containers consist of a floor structure with a high loading capacity composed of a steel frame and a softwood floor and two end walls, which may either be fixed or collapsible.(7)
Flatrack containers consist of a floor structure with a high loading capacity composed of a steel frame and a softwood floor and two end walls, which may either be fixed or collapsible.(7)
The end walls are stable enough to allow cargo securing means to be attached and several flatracks to be stacked on top of one another.
Flatracks are available in 20′ and 40′ sizes.
The flat racks with collapsible ends also permit the transportation of over length cargo.
Flatrack Container Dimensions: 20′ Open Top Container, 40′ Open Top Container and
40′ Open Top High Cube Container dimensions.
Flatrack Container Dimensions: 20′ Flatrack Container and 40′ Flatrack High Cube dimensions.
Platforms:
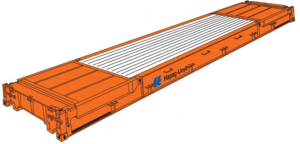 Platforms consist solely of a reinforced floor structure with extremely high loading capacity; they have no side or end walls. (8)
Platforms consist solely of a reinforced floor structure with extremely high loading capacity; they have no side or end walls. (8)
Platform containers are ideally suited to oversized, heavy load and awkward project cargoes which cannot be transported in other container types such as high cube or open top containers. (9)
Platform containers can be lashed together to create a larger platform for oversized and heavy loads which exceed the standard platform container specifications.
Platform containers are available in 20ft and 40ft sizes.
Platforms Dimensions: 20′ Platform and 40′ Platform dimensions.
Bulk Containers:
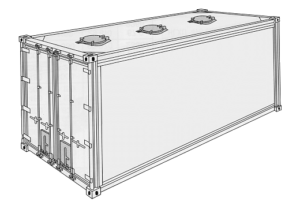 Bulk containers have three loading hatches in the roof, each of a diameter of approx. 455 mm (1 3/4′).
Bulk containers have three loading hatches in the roof, each of a diameter of approx. 455 mm (1 3/4′).
On the door side, there are two discharge hatches, which are sometimes equipped with short discharge tubes for guiding the bulk cargo.
Alternatively, two unloading hatches may be mounted in the doorways, for emptying the containers.
Such containers may also be used for general cargo. Lashing rings are mounted in the top side rails for securing the cargo. Some bulk containers are equipped with forklift pockets, which allow handling by forklift trucks. (10)
References:
- Export911.com | Shipping Department, Logistics Management, Freight Containers
- Export911.com | Shipping Department, Logistics Management, Freight Containers
- Containerships website regarding dry containers
- Containerships website regarding reefer containers
- Understanding reefer containers and refrigerated shipments, Advanced on Trade website.
- Hardtop Containers, Transport Information Service (TIS)
- Flatrack Containers, Transport Information Service (TIS)
- Platforms, Transport Information Service (TIS)
- Platform Shipping Container Specifications, Tuscor Lloyds
- Bulk Containers, Transport Information Service (TIS)


















